I’ve been working for some time with Linux and I feel that sharing some scripts and also tools I frequently use can be helpful.
Search History
history | grep seach_string
or Ctrl+R.
Search Log files
In order to search a folder to see if a string exists in the whole folder:
grep -ir "string to search" .
Show File and Folder Size
To analyze file size, there are several ways.
ls -alh
-rw-r--r-- 1 amir amir 270K May 20 2023 Arial.ttf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 72 Sep 20 21:10 Untitled5.ipynb
-rw-r--r-- 1 amir amir 1.2M May 26 2023 exp12.mp4
-rw-r--r-- 1 amir amir 4.7M May 26 2023 exp13.mp4
-rw-r--r-- 1 amir amir 654M May 22 2023 exp4.avi
-rw-r--r-- 1 amir amir 68 Dec 28 2022 kaggle.json
drwxr-xr-x 17 amir amir 4.0K Dec 28 2022 miniconda3
drwxr-xr-x 2 amir amir 4.0K May 26 2023 mp4
You can see from the above output that this only shows file sizes properly.
On folders, I use:
du -h --max-depth=1
(Optional) To sort it:
du -h --max-depth=1 | sort -hr
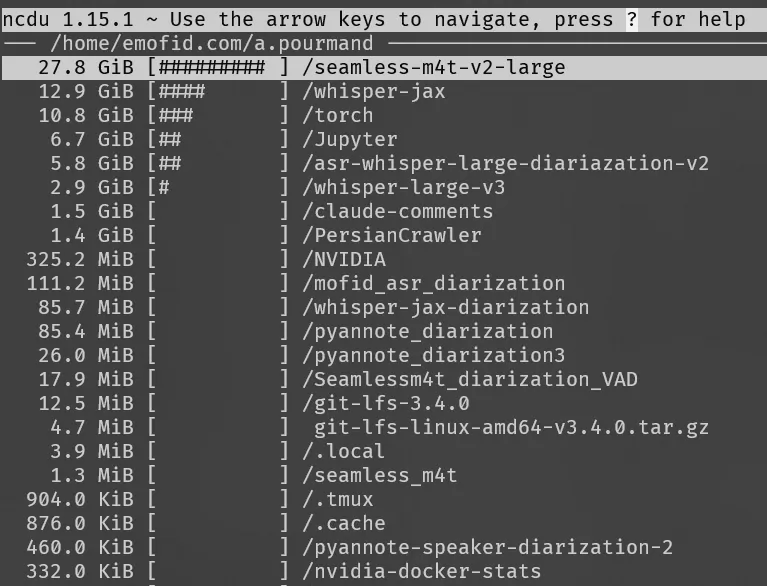
Of course, this is when I do not have access to sudo. In case of sudo access, I will pretty much always install ncdu via:
sudo apt install ncdu
This way, I would be able to easily navigate between folders and find out which folder is taking the most space.
Test Access to a Server or Service
This is especially the case in big companies when you should request access for a server. They may give the network access to you but not SSH access. Or you may just want to troubleshoot your network and what not.
ping ip
telnet ip port
nc -v ip port
for example:
ping 10.2.10.4
telnet 10.2.10.4 22
nc -v 10.2.10.4 22
Show Network Ports Already being Used
This is especially useful for docker images when you want to spin up a docker image and you want to specify a new port to it.
netstat -nlpt
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8017 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8019 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8018 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8081 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8080 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.53:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 :::8017 :::* LISTEN -
tcp6 0 0 :::8019 :::* LISTEN -
Get Server Information
Logged in users:
w
IP Address:
ifconfig -a | grep inet
Hostname:
cat /etc/hostname
Linux Kernel:
uname -a
Disk Space:
df -h
Memory and CPU usage:
htop
or maybe just install Neofetch.
Useful Terminal Tools to install
Watch Network Usage
sudo apt install iftop
Enable SSH Access to system
sudo apt install openssh-server
This way you can access your laptop (or server) via SSH easily.
Manage Backup
I frequently use this one to create and restore backups from my folders.
Create Backup (don’t forget sudo if necessary):
tar -czvf volumes-$(date +%Y.%m.%d.%H.%M.%S).tar.gz volumes
Restore Backup:
tar -xzvf volumes-2024.08.18.15.05.57.tar.gz
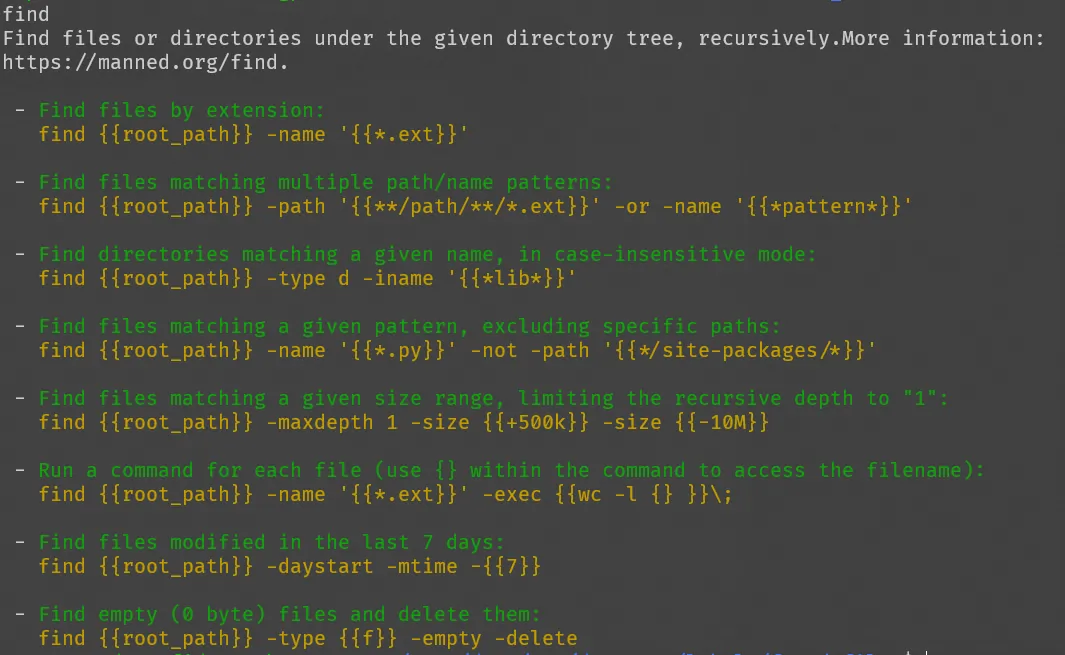
Find Documentation for a command
Let’s say you want to read documentation for a command like find. You might do man find or find --help but none of them are easy to read. We can do better.
sudo apt install tldr
tldr --update
Install tldr (too long didn’t read) and then use tldr find. This way you would find a much better and easy to follow documentation. Just take a look at it. Isn’t that better? (+ / +)
Or, If you don’t want to install anything, you can just use cheat.sh like this:
curl cht.sh/tar
curl cheat.sh/tar
Also, see GitHub - jlevy/the-art-of-command-line: Master the command line, in one page.
Must see tutorial about shell scripts:
For my purposes, I just add these these lines in any script I am writing:
#!/bin/bash
set -euo pipefail